flexVDI is a Desktop Virtualization platform. Its main goal is to provide your users with ubiquitous access to their desktops. Whether they connect from a personal computer or their mobile phone, from the room next door or from hundreds of kilometers away, with flexVDI your users will experience their desktops as if they were right in front of them. Using well-known, open-source technologies, it provides a stable, performant infrastructure for both Windows and Linux desktops.

flexVDI main features are:
- Supports virtualization of Windows from XP to Windows 10, Windows Server 2003 and upper versions, and all flavors of GNU/Linux. We can advice you on the best way to configure your guest operating systems so that your users get the most of their desktops.
- Desktops are accessible from a wide variety of clients. There are Windows, Linux and Mac desktop clients, as well as mobile clients for iOS and Android devices. We also provide a Linux distribution prepared to boot a thin client directly into your flexVDI desktop. Finally, you can even access your desktop from anywhere using just a web browser with our HTML5 client.
- Scalable, fault-tolerant cluster architecture. New hosts can be added to the cluster as needed, as easily as configuring the network and registering the host with the platform. Its resources will be ready to use at once. In the same way, the platform will quickly recover from a host failure, using the rest of its resources to keep the service up and running. Growing from hundreds to thousands of desktops is easy with flexVDI.
- Binary packages are provided for RHEL 7 and CentOS 7. Your hosts will benefit from the reliability and experience of Red Hat operating systems.
- Uses Qemu/KVM as the virtualization engine and Spice as the presentation protocol, with additional improvements to boost your VDI experience.
- Template-based desktops. Quick and easy to update when new versions of your software are available, highly available when malicious software threats your desktop instances.
- LDAP or AD based authentication/authorization. flexVDI integrates with your corporate directory.
- Configurable security capabilities, to restrict access to the desktop resources from the client side: clipboard, printers, usb devices, ...
- Supports shared storage like SAS, FC, iSCSI, etc...
flexVDI must be installed on a set of physical servers with either RHEL 7 or CentOS 7, that form a VDI cluster. Installing it in a virtual machine managed by a different hypervisor is not supported. This document will guide you through the process of installing flexVDI 3.1 on your physical servers.
Terminology
This document makes use of various virtualization and flexVDI specific concepts. Below you will find those terms with a brief description:
- Guest: A virtual machine defined by a given configuration, some host resources and one or more disk images.
- Host: Each one of the physical servers devoted to run Guests. The flexVDI software is installed on these machines.
- Pool: collection of resources (CPU and, RAM) allocated in each Host
- Template: A special type of Guest, whose logical content is frozen in order to generate Clones.
- Clone: A special type of Guest, created from a Template, that shares part of its configuration with the later. Disk images from Clones only store the differences between its current state and the state of their Template.
- Image Storage: Set of disks available for storing the disk images that Guests use. It is divided in several Volumes. One Image Storage is only available to those Hosts that can access all of its disks.
- Internal Volume: Component of a Image Storage that provides disk space for the Guests Images. The cluster filesystem used in a Volume is created and managed by flexVDI software. Uses a block device as its physical support.
- External Volume: Hosts directory path where Guests images are stored. The directory can be local or it can be a mount point from an external storage system. External Volumes are installed and managed by the system administrator using the tools provided by the manufacturer of the storage.
- Media Storage: Shared resource where ISO images are stored.
- Direct Storage: Option used to provide a Guest direct access to physical disks.
flexVDI Architecture
A flexVDI platform consists of a set of hardware and software components that interact with each other to provide a satisfactory Virtual Desktop experience. From the hardware point of view, there must exist one or more computational nodes, called Hosts, and one or more storage objects. The Hosts provide the CPU and RAM resources needed to run the virtual desktops, while the storage objects contain their disk images.
On the other hand, the basic software components are:
- flexVDI Manager: The orchestrator that centrally manages and configures all other components. It is distributed in a disk image, and runs as a Guest inside one the Hosts. The Guest containing the flexVDI Manager instance can be moved to any Host of the infrastructure, increasing availability and resilience for the environment.
- flexVDI Agent: A service running on each Host that manages its local resources on behalf of the flexVDI Manager instance. It controls the availability of CPU and RAM, the life cycle of the Guests running in the Host and the storage objects it can access.
- flexVDI Config: Tool available on all Hosts, which can be used for configuring them and the flexVDI Manager instance.
- flexVDI Dashboard: Web application that allows the platform administrators to see the platform, for instance see active connections, storage status, memory usage ... and also create new guests, and other operations.
- flexVDI Client: Desktop presentation tool that allows end-users to access their virtual desktop. There are several native versions for different platforms: Windows, OS X, Linux, Android, iOS, and a live Linux distribution for x86/amd64 terminals.
- flexVDI Guests: These are the virtual machines that actually contain the desktops. Each Host runs a set of Guests, according to its available resources and the Guests' needs. The flexVDI Manager instance is a special kind of Guest.
The most simple configuration of a flexVDI platform, looks like this:
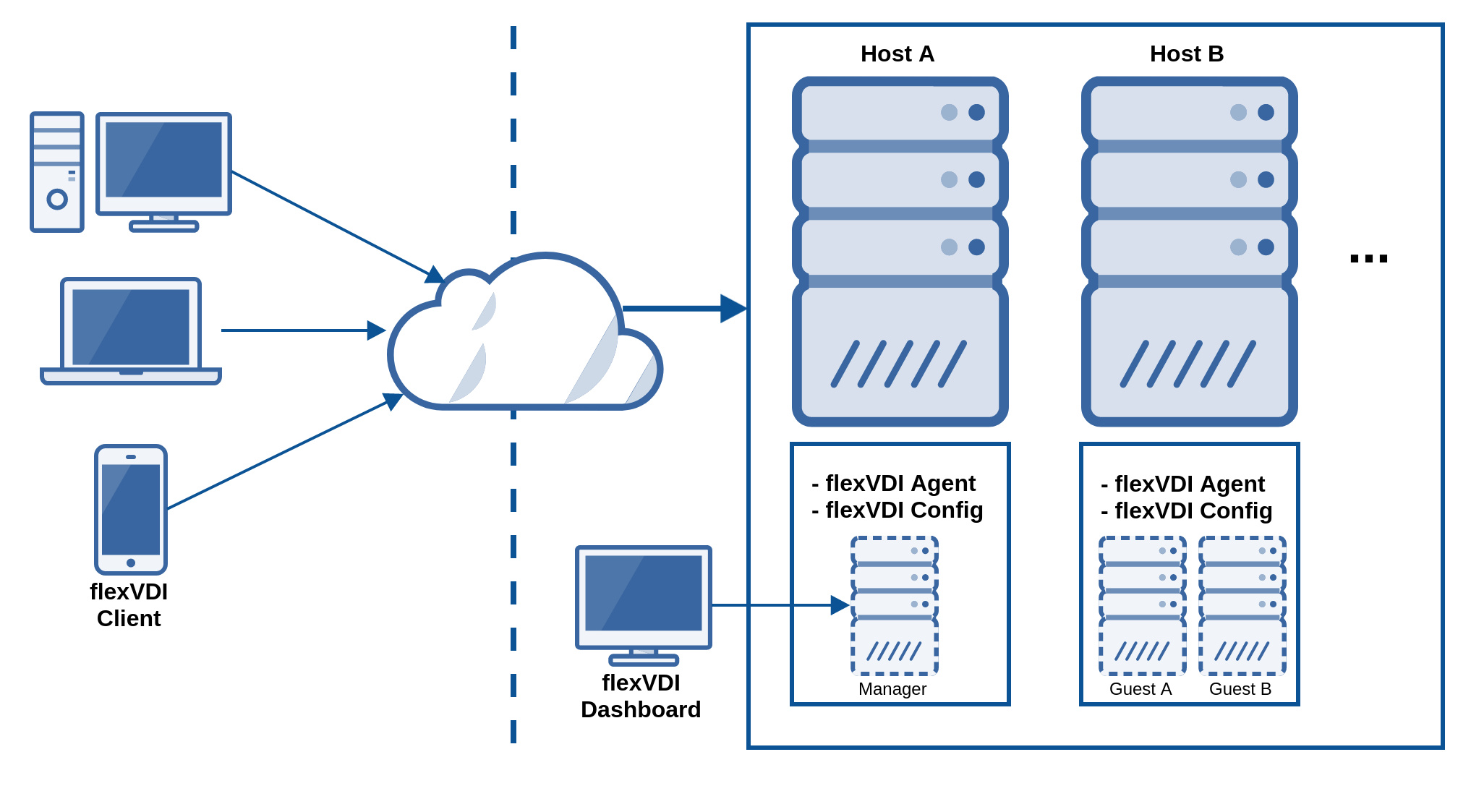
A flexVDI Agent runs on each Host, while only one flexVDI Manager instance controls the platfrom. The flexVDI Config tool configures individual Hosts, while the flexVDI Dashboard application manages the platform logic, interacting directly with the flexVDI Manager. Finally, the flexVDI Client is the end user viewport to a virtual desktop.
Additionally, flexVDI offers the following components for additional features:
- flexVDI Gateway: Platform entry point for flexVDI Clients. It encapsulates all communications with WebSockets over TLS to a single public TCP port, easing network administration and providing secure communications. It can scale horizontally when required by massive deployments.
- flexVDI WebPortal: Appliance composed of a flexVDI Gateway and a flexVDI HTML5 Client application. Provides access to virtual desktops from web browsers where installing a native client is not possible.
- flexVDI Guest Tools: Set of tools that provide improved performance and extra functionality (printer sharing, clipboard sharing, USB device redirection) to the Guest where they are installed. There are Windows and Linux versions available


