Storage
In the second drop-down The second section of the main window tree , view contains the storage infrastructure is shown. flexVDI Infrastructure supports objects of a flexVDI platform. There are three kinds of storage Objectsobjects: Image Storages
...
, Media Storages
...
and Direct Storages.
Image Storage
The Image Storage objects are logical storage units. Another way to see a Image Storage is like a like a container volumes. This Volumes represent a logical storage space for Guests' images, accessible by a set of Hosts. This space is further divided into Volumes, which store the virtual disks of the Guests. Each Image Storage is created in all selected Host.
The typical use of an Image Storage is to map a shared disk array and its volumes to the set of Hosts connected to it. flexVDI supports the most common SAN technologies: SAS disk arrays, Fiber Channel, iSCSI...
Clicking on one Image Storage, will show us information about it in the right area of the main screendetails view. The following figure shows an example.
Under the "Host List" title, there is a list with the Hosts that can access this Image Storage. This detail is important because the Guests whose virtual disks (disk images from the perspective of Host) are housed in this Image Storage may run on any of these Hosts. This enables high availability of Guests.
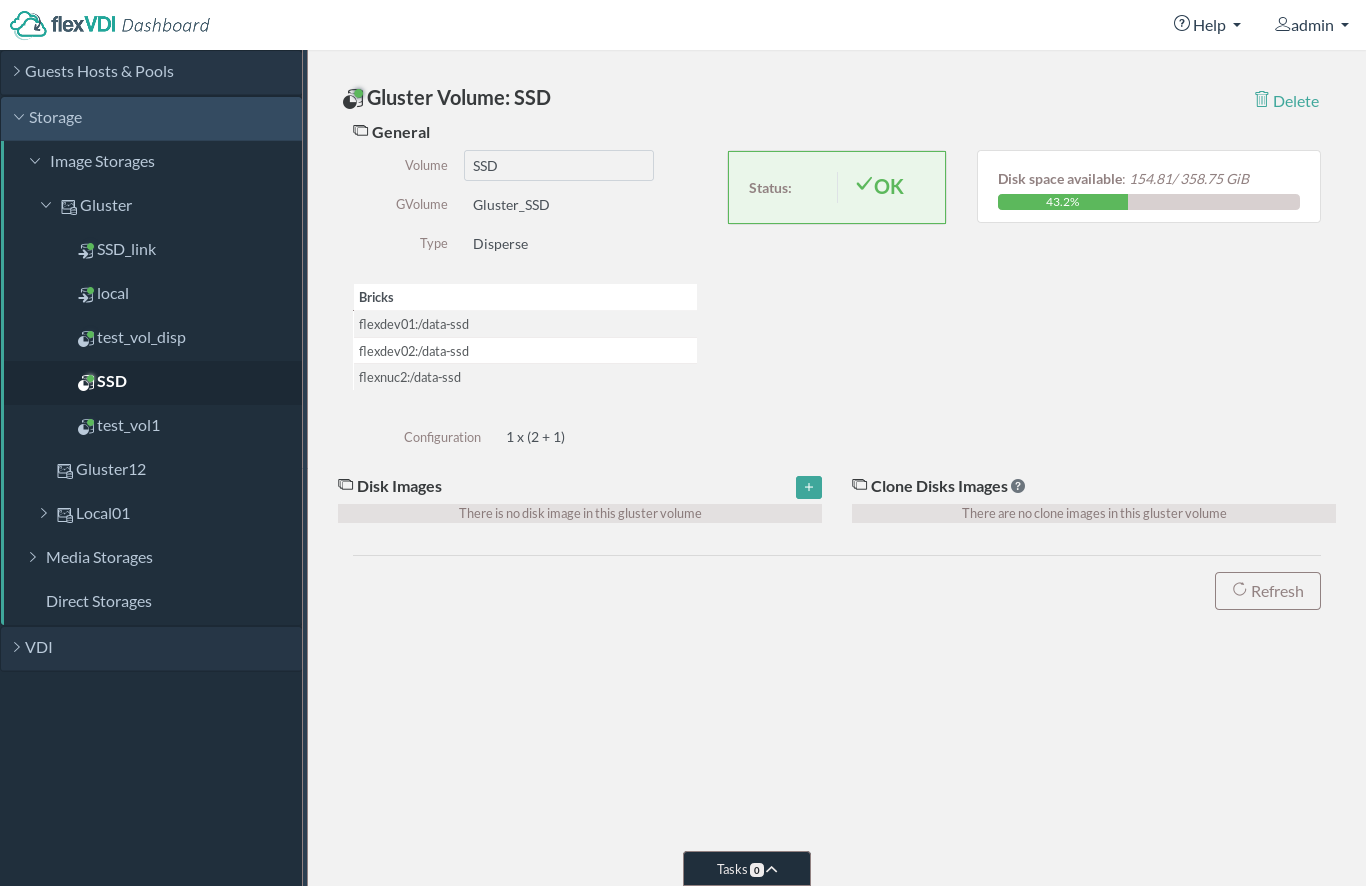
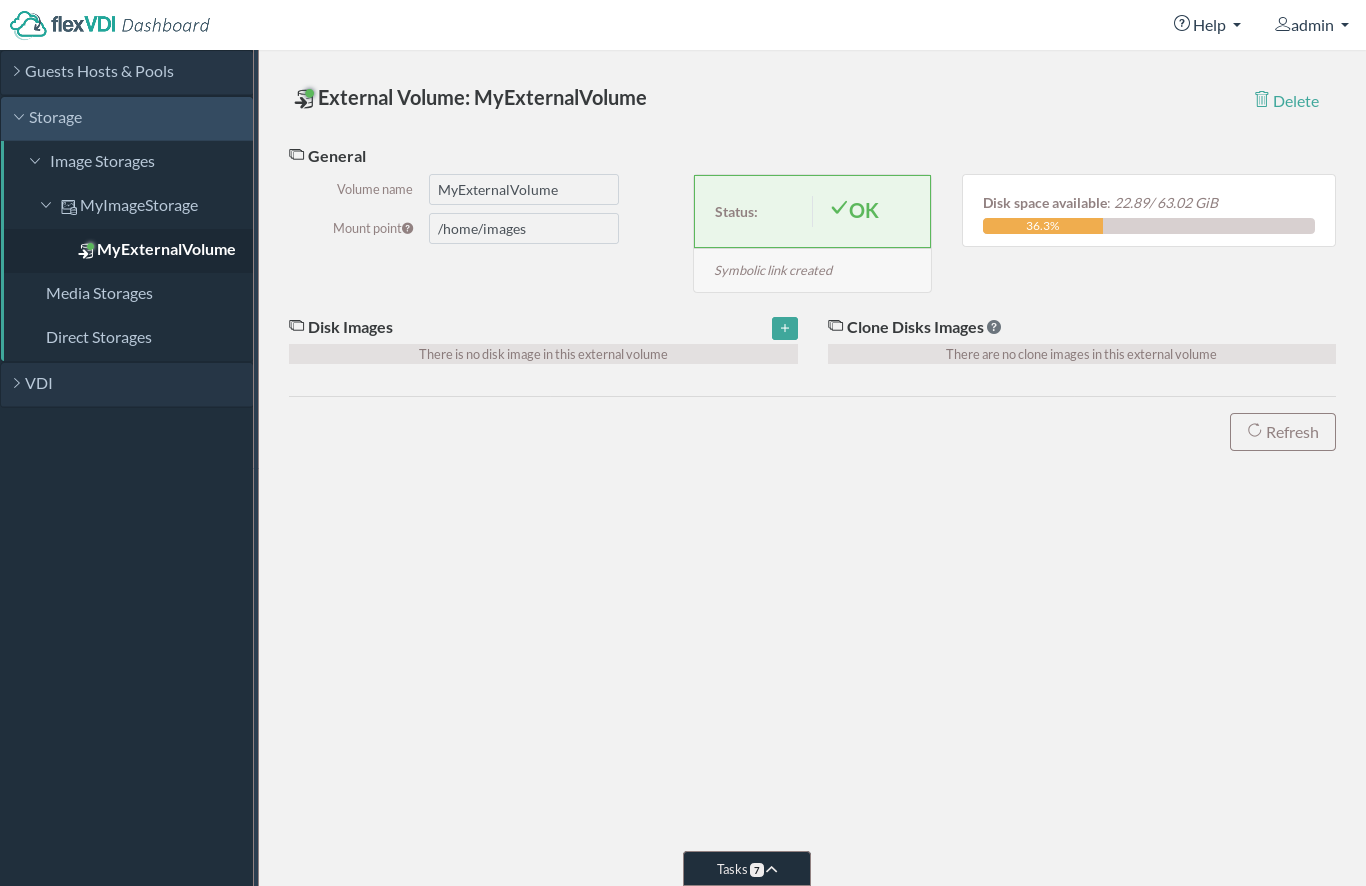
Within an Image Storage you can create two thre types of Volumes: OCFS2 Volumes, Gluster Volumes and External Volumes.
OCFS2 Volume
OCFS2 Volumes (not external) are managed by the infrastructure.flexVDI software formats and mounts the discs. In return, the configuration possibilities are more limited. are created with a block device that is shared by all the Hosts of the Image Storage (e.g. an iSCSI LUN or SAS disk connected to all the Hosts) and formated with the OCFS2 filesystem. This is a cluster filesystem that can be mounted by all the hosts simultaneously. In order to set up the cluster, please refer to the section about OCFS2.
Gluster Volume
Gluster Volumes use the GlusterFS distributed storage technology to aggregate several local disks into a single storage space. This solution does not need to access a shared volume in a SAN and uses cheaper, more common hardware, but its performance is lower. You need at least two hosts to create a Gluster Volume.
| Warning |
|---|
Gluster Volumes are an experimental feature. Stability and performance issues have been observed, so use it at your own risk. |
External Volume
External Volumes are created and managed by the system Administrators, which gives them total flexibility. A system administrator has to connect log in to the Hosts and, using the tools provided by the operating system or hardware manufacturer, connect, format, and mount the storage in the Hosts. After completing the configuration and mounting the storage hardware. Then, you can create an External Volume, which that simply points to the directory where the storage is mounted. This will allow flexVDI to create virtual disks on it. If you are configuring a cluster to enable Guests to run on more than one Host, all of these Hosts must be able to access the storage on the same path (mount point). That mount point is the one entered in flexVDI Dashboard .
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Be careful that the |
...
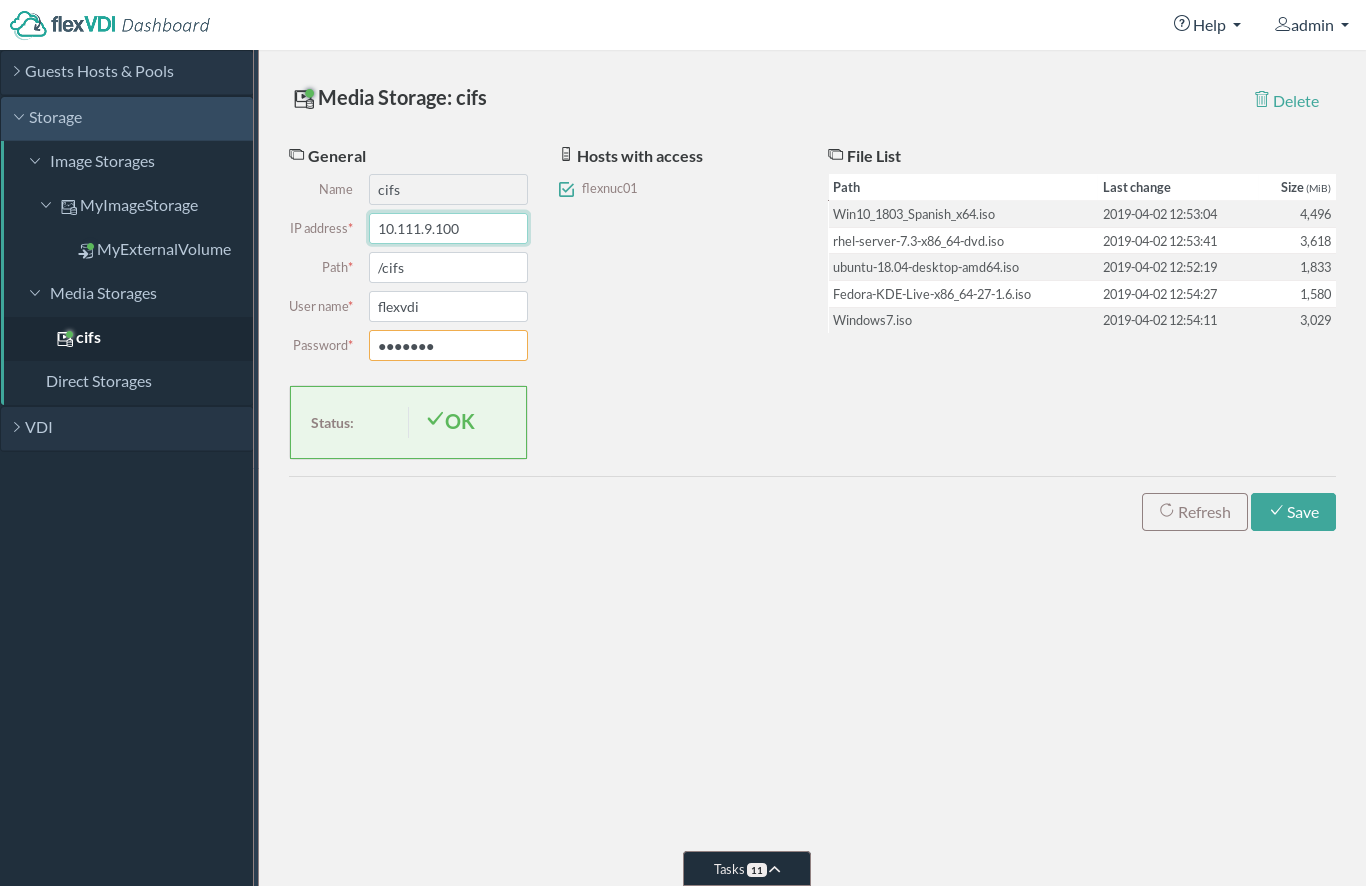
Media Storages
Media Storages are repositories of ISO image files. These files can be mounted as optical disks by Guests and are useful , e.g. for the initial installation of the OS, and more. When clicking on a Media Storage, information about it will be displayed in the right areadetails view. The following figure shows the displayed information.an example:
Direct Storages
Direct Storage provides Guests direct access to the physical disks. Clicking on a Direct Storage, will show information about it in the area on the right. The following figure shows the information.
The details view:
TODO: Screenshot
A Direct Storage provides improved performance by eliminating the middle layer of storage virtualization, at the cost of loosing its additional functionality (easy copy of images, incremental disks, ...)
...