This section explains how to configure your platform so that flexVDI clients are able to connect and present a virtual desktop. Several configurations are possible, from simple ones where clients are able to reach any host of the platform, to more complex ones where hosts are not directly accessible (e.g. they are behind a firewall or NAT router). Here, you will understand these possibilities and their implications, and how to select the configuration that best fits your corporate network.
...
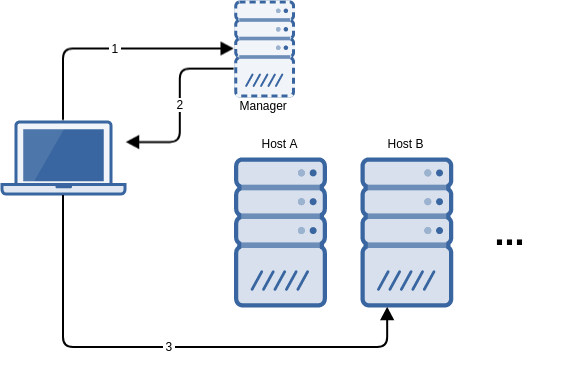
- The client contacts the manager, identifies itself as a terminal and, optionally, authenticates the user.
- The manager decides which desktop to assign to the user, and returns the connection parameters to the client; in particular, the address of the host where the desktop is running and the Spice port.
- The client connects to the desktop at the supplied host with the Spice protocol.
As a result of this conversation, the client must be able to contact the manager as well as every potential host where the desktop may be running. This basic configuration may be suitable when clients are connecting from an internal network.
...
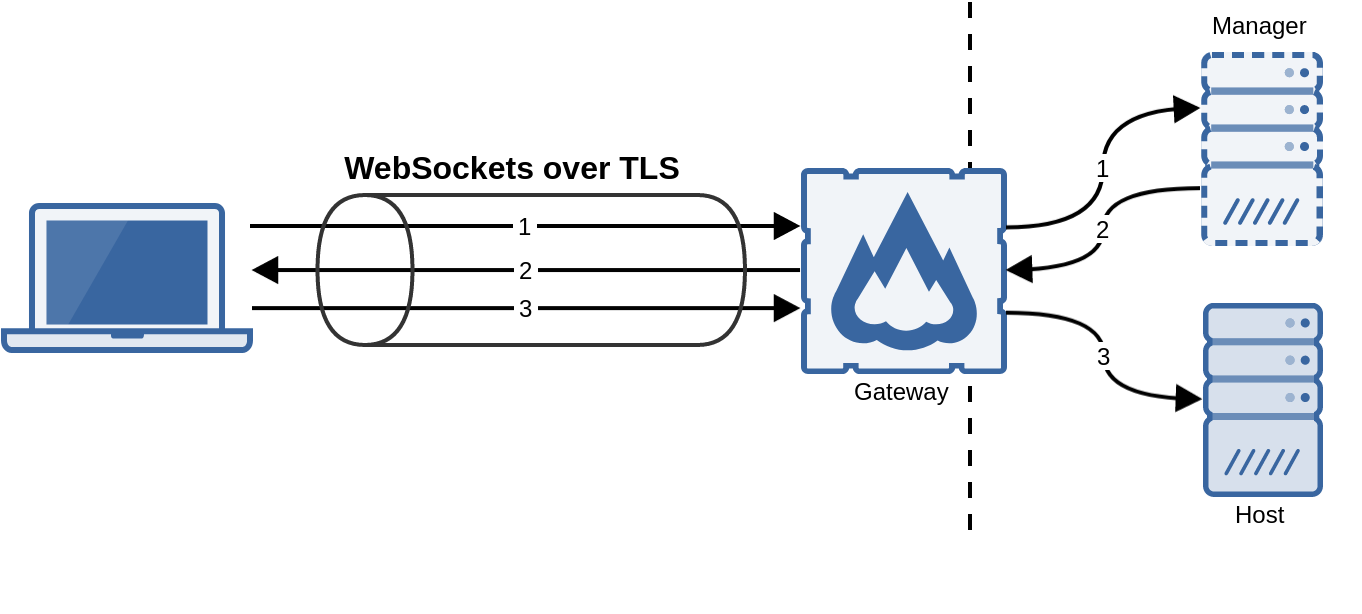
The flexVDI Gateway is a software component that overcomes this limitations by encapsulating all the traffic, either to the manager or the desktop, with WebSockets over TLS encryption at port 443:
In this way, only TCP port 443 (or the port you configure) of the machine that runs the gateway must be exposed to the clients.
...
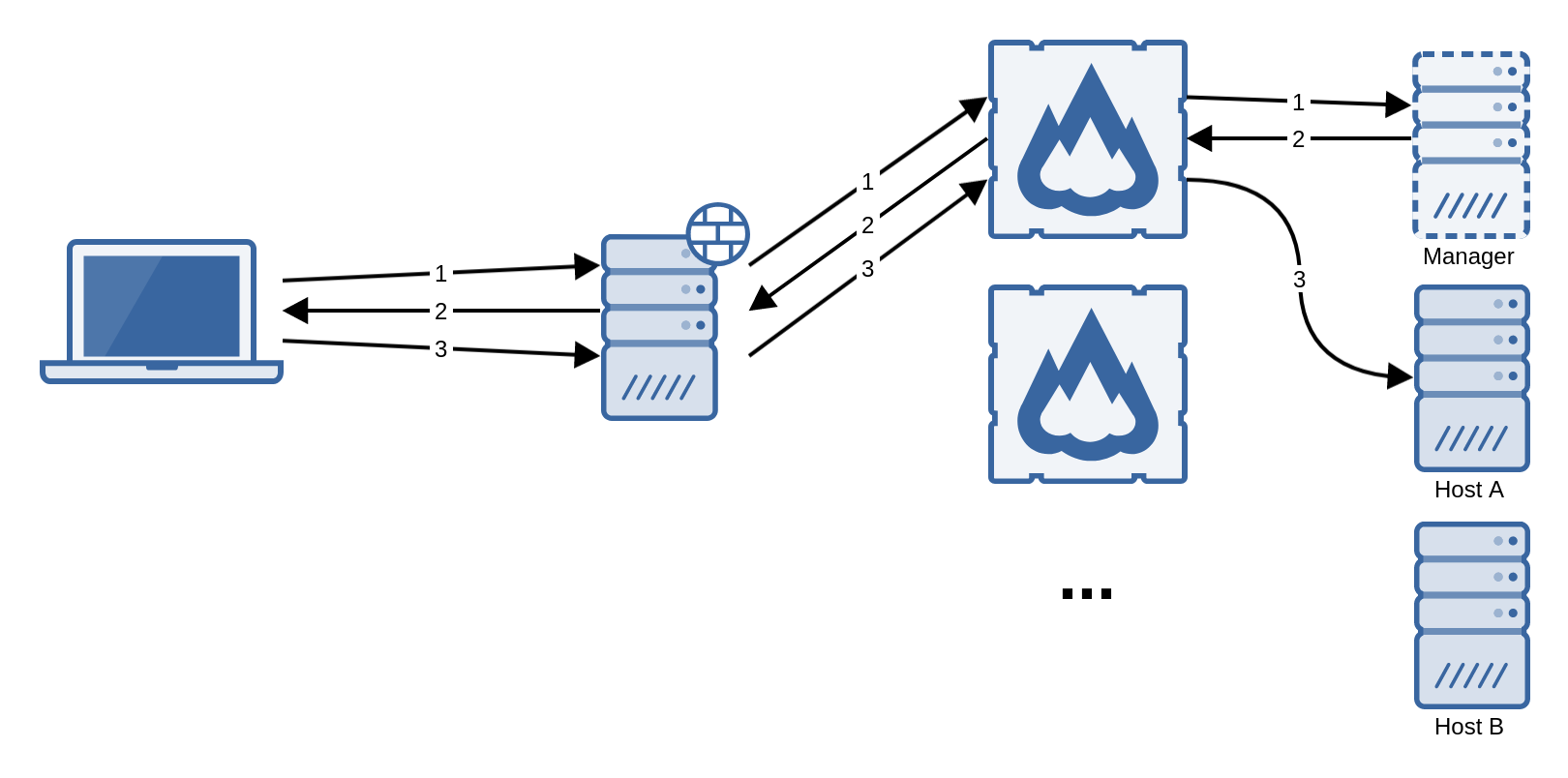
It is possible to use a web load balancer to distribute the client connections among several flexVDI Gateway instances. However, in order for this scenario to work, sequential connections of the same client must be assigned to the same gateway. This can be done, for instance, assigning the gateway by source address.
Connecting through a reverse HTTPS proxy
...